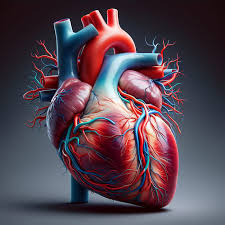
The human heart, a fist-sized organ, is more than just a symbol of love and emotion—it’s the engine that keeps us alive. Pumping tirelessly from the moment we’re born until our last breath, the real human heart is a masterpiece of biological engineering. Let’s take a closer look at this incredible organ and what makes it so vital to our existence.
Anatomy of the Human Heart
The human heart is located slightly to the left of the center of the chest and is protected by the ribcage. It’s divided into four chambers:
- Two Atria: The upper chambers that receive blood—the right atrium takes in oxygen-depleted blood from the body, while the left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs.
- Two Ventricles: The lower chambers that pump blood—the right ventricle sends blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen, while the left ventricle pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
The heart is equipped with valves—tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic—that ensure blood flows in the correct direction. These valves open and close with each heartbeat, producing the familiar “lub-dub” sound.
How the Heart Works
The human heart is essentially a muscular pump. Here’s how it functions in a continuous cycle:
- Filling: Blood flows into the atria from the body and lungs.
- Pumping: The atria contract, pushing blood into the ventricles. The ventricles then contract, sending blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
- Resting: Between beats, the heart relaxes, allowing the chambers to refill with blood.
This cycle occurs about 100,000 times a day, moving nearly 2,000 gallons of blood through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries.
The Heart’s Electrical System
The heart’s rhythm is controlled by its own electrical system. The sinoatrial (SA) node, often referred to as the heart’s natural pacemaker, generates electrical impulses that trigger contractions. These impulses travel through the heart’s conduction pathways, ensuring the chambers contract in a coordinated manner.
Keeping the Heart Healthy
A healthy heart is essential for overall well-being. Here are some tips to maintain cardiovascular health:
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week to strengthen the heart muscle.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limit sodium, sugar, and saturated fats.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure and other heart-related issues. Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Regular Check-Ups: Monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall heart health with routine medical visits.
Fascinating Facts About the Human Heart
- The heart beats about 2.5 billion times in an average lifetime.
- The left ventricle—the heart’s most powerful chamber—can create enough pressure to squirt blood up to 30 feet.
- The heart starts beating about three weeks after conception.
- A woman’s heart typically beats faster than a man’s.
Advances in Heart Research
Modern medicine continues to revolutionize our understanding of the human heart. Innovations such as artificial hearts, stem cell therapy, and advanced imaging techniques are saving lives and offering hope to those with heart conditions. Additionally, lifestyle-focused approaches emphasize prevention, helping people avoid heart disease altogether.
Final Thoughts
The real human heart is a marvel of nature—a tireless, intricate machine that sustains life. Understanding how it works and taking steps to protect it can help ensure a long, healthy life. Whether you’re inspired by its symbolism or fascinated by its biology, there’s no denying the extraordinary importance of the human heart.